What is Oracle NetSuite ERP?
Oracle NetSuite is a cloud-based enterprise resource planning (ERP) software suite used by businesses of all sizes. It provides a comprehensive set of modules to help manage finances, operations, customer relationship management (CRM), inventory, and more. Its core modules are designed to help optimize financials and operations, while its advanced modules offer customizability and flexibility.
Oracle NetSuite also offers integration and customization options, allowing businesses to connect their existing business systems and customize workflow to meet their specific needs. Additionally, Oracle NetSuite provides industry-specific solutions for retail, manufacturing, and services businesses.
Introduction to NetSuite Integration
One of the key benefits of using NetSuite is its ability to integrate with other systems and applications. In this blog, we will explore the various ways in which NetSuite can be integrated and the benefits of doing so.
Methods for Integrating NetSuite
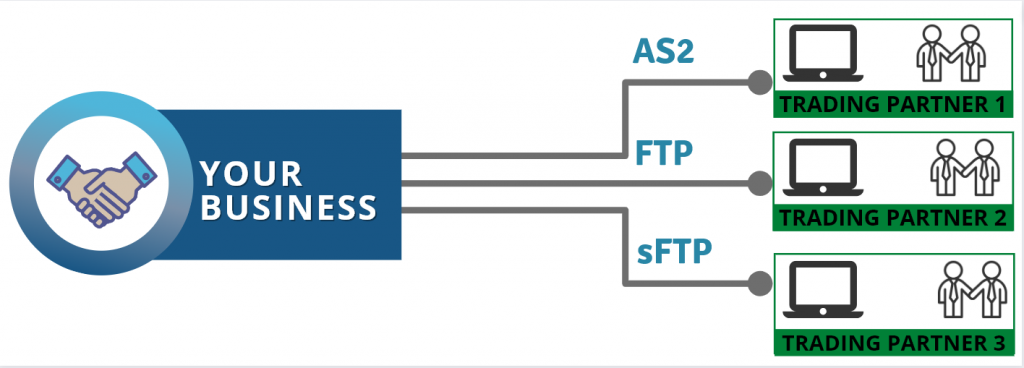
There are several methods for integrating NetSuite with other systems. One of the most common methods is through the use of APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) or web services. NetSuite offers a range of web services, that allow developers to build custom integrations between NetSuite and other systems. These web services can be used to extract data from NetSuite, update records, or trigger actions within the system.
To efficiently integrate with NetSuite, we recommend the use of third-party integration platforms like Magic xpi.
USEFUL READING: Magic xpi Integration Platform: The Best Fit for Enterprise Data Integration
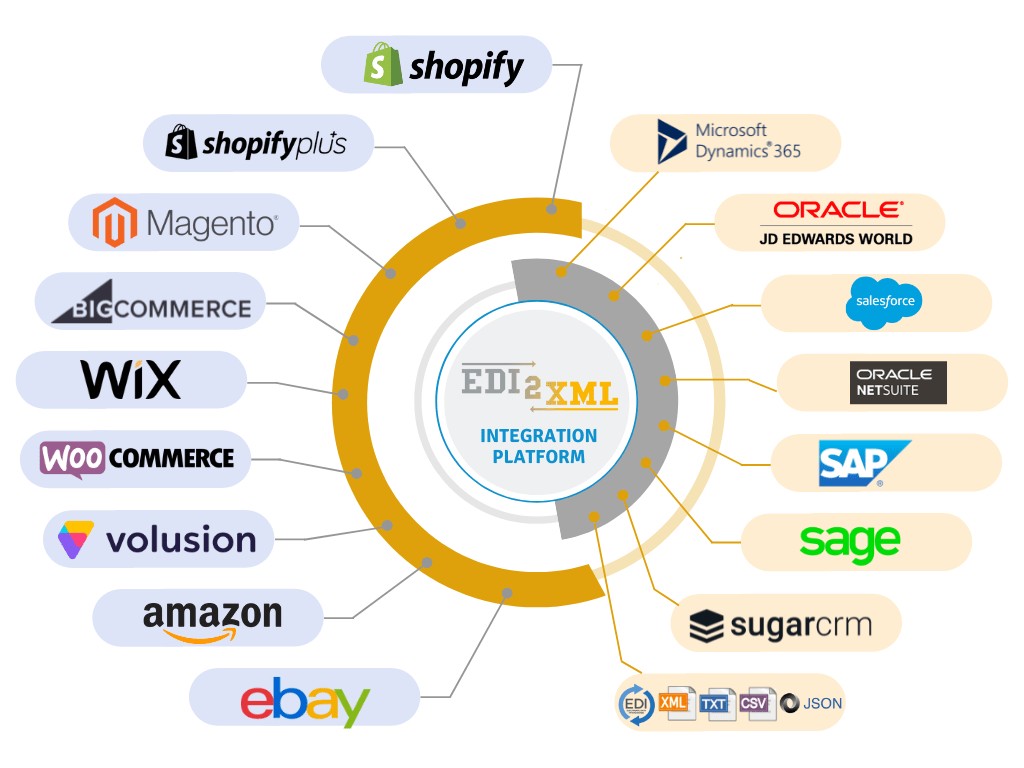
Magic xpi integration platform provides pre-built connectors to easily connect NetSuite with other applications and business systems such as Salesforce, SAP, Microsoft Dynamics, and many more. This can be a quick and cost-effective way to integrate with NetSuite, as the connectors are pre-built and require little configuration.
NetSuite Integration with E-commerce
Oracle NetSuite integration with e-commerce platforms such as BigCommerce, Magento, Shopify or Amazon allows businesses to streamline their online operations and improve customer experience. With the integration, businesses can easily manage their entire e-commerce operations cycle from a single platform. It allows businesses to track orders, inventory, customers, and payments all in one place.
USEFUL READING: E-commerce integration: How to integrate Shopify, BigCommerce, Magento, with ERP/CRM systems
The integration also provides businesses with access to powerful analytics tools that help monitor and analyze customer behavior and preferences. The integration of business systems and e-commerce helps track and analyze orders and customer preferences. This allows companies to improve their e-commerce operations and customer experience.
EDI Integration with NetSuite
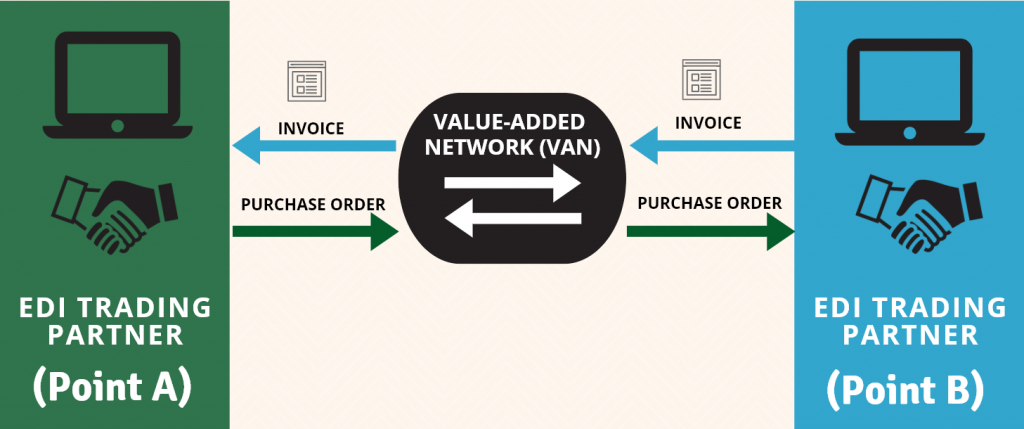
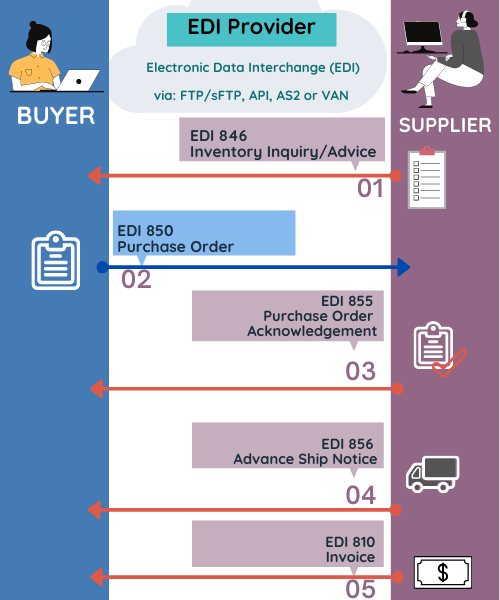
EDI (Electronic Data Interchange) is a common method for exchanging business information such as purchase orders (EDI 850), invoices (EDI 810), Inventory Inquiry/Advice (EDI846) and many more EDI documents electronically.
One way to integrate NetSuite with EDI is to use Fully Managed EDI Service. This service allows incoming EDI documents to be converted into a format that can be processed by NetSuite. Fully Managed EDI service ensures that all incoming EDI documents are automatically imported into NetSuite without requiring manual data entry. For outgoing documents, the managed EDI service converts them to the required format (e.g. X12) and sends them to your business partner.

Alternatively, businesses can use an HTTP EDI Web Service (REST API) to integrate EDI with NetSuite. Companies can use the EDI2XML REST API service to send and receive EDI documents such as invoices, purchase orders and other. The API supports X12 and EDIFACT standards, as well as other EDI document standards.
Regardless of the method used, integrating NetSuite with EDI can help businesses streamline their operations and reduce the need for manual data entry and document handling.
Benefits of Integrating NetSuite
There are several benefits to integrating NetSuite with other management systems, application, ecommerce, or EDI. One of the most significant benefits is the ability to share data across systems. By integrating NetSuite with other applications, businesses can avoid the need to manually enter data into multiple systems, which can save time and reduce the risk of errors.
Integration can also improve the accuracy and quality of data. By connecting NetSuite with other systems, businesses can ensure that all data is up to date and consistent across all systems. This can be especially useful for companies that rely on real-time data for business operations or decision-making.
Another benefit of integrating NetSuite is the ability to automate processes. By connecting NetSuite with other systems, businesses can set up automated workflows that trigger actions or updates in one system based on events or data changes in another system. This can help businesses streamline their operations and reduce the need for manual intervention.
NetSuite Integration: Conclusion
In conclusion, NetSuite integration is a powerful way for businesses to improve efficiency, accuracy, and automation. By connecting NetSuite with other systems and applications, businesses can share data, improve the quality of data, and automate processes. Whether through APIs or third-party integration platforms, NetSuite integration is an important consideration for businesses looking to get the most out of their technology investments.